Why Image Optimization Matters for SEO
Images play a crucial role in on-page SEO, affecting website speed, user engagement, and search engine rankings.
Optimizing images can enhance your website’s performance in several ways. Images can take up a large portion of a website’s data, slowing down load times, which negatively impacts user experience and your SEO ranking. Faster-loading pages lead to better user engagement and higher rankings. Search engines like Google also crawl and index images, using metadata to determine relevance and context.
With the shift toward mobile-first indexing, it’s more critical than ever that images are optimized for mobile devices. This ensures your site loads efficiently across all platforms, providing a seamless experience for users, which search engines reward.
1. Use Unique Images (When Possible)
While stock images serve a purpose, unique images can provide a distinct advantage in SEO. Original images, such as custom photos, infographics, or illustrations, offer something new to users and are less likely to be duplicated across the web.
Search engines tend to favor unique content, including images. They add value, create a sense of originality, and can make your brand more memorable. Plus, unique visuals can boost engagement by better aligning with your content, which can lead to longer time spent on your page—a metric search engines look at when ranking websites.
2. Choose the Right Image Format
The choice of image format can significantly affect both quality and performance. SEO recommended image file formats include:
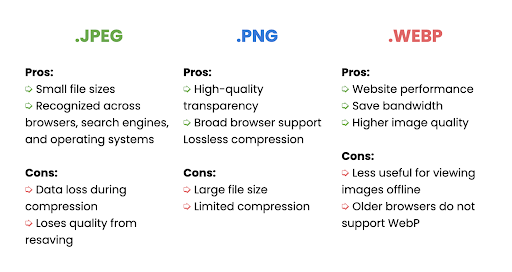
- JPEG is commonly used for photographs due to its high compression, though some quality loss occurs.
- PNG is ideal for images requiring transparency or more detail, though it results in larger file sizes.
- WebP, a newer format, provides both excellent quality and smaller file sizes, making it great for performance.
Choosing the right format depends on the content of the image—JPEG for large, detailed photos, PNG for logos and graphics with transparency, and WebP for a balance of quality and size across different types.
3. Resize Images
Oversized images can drastically slow down your website, leading to poor user experience and lower rankings. Resizing images to fit their intended display size ensures they don’t unnecessarily consume bandwidth. For example, if a space requires a 300px-wide image, uploading a 1500px-wide image wastes resources.
For larger images that need to be displayed, lazy loading is a great solution. It defers the loading of offscreen images until they are needed, reducing initial load times and enhancing the user experience.
4. Compress Images Without Losing Quality
Compressing images is essential for reducing file sizes while maintaining visual quality.
Tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or ShortPixel can significantly decrease image file sizes, which improves page speed and overall performance. Compression should be applied in a way that preserves as much visual clarity as possible. The goal is to find the right balance—retaining quality while minimizing size.
Combining compression with lazy loading creates a seamless experience, ensuring your website loads efficiently without compromising on image quality.
5. Create Descriptive and SEO-Friendly File Names
File names play a crucial role in SEO as they help search engines understand the content of the image. Best practices for naming images include descriptive file names containing relevant keywords can improve your chances of appearing in image search results.

For example, instead of naming the above image “IMG001.jpeg,” use something like “niagara-falls-rainbow.jpeg” to provide context. File names should be short, use hyphens to separate words, and align with the content of the page. This approach not only helps with SEO but also keeps your image library organized.
6. Optimize Alt Text for SEO and Accessibility
Alt text serves two important purposes: it improves accessibility for visually impaired users and it helps search engines understand the content of an image. When writing alt text, describe the image accurately and include relevant keywords, but avoid keyword stuffing.

For example, instead of just saying “ice cream,” use something like “holding ice cream cone by the boardwalk”
Well-crafted alt text not only enhances user experience but also increases the likelihood of your images appearing in image search results, boosting overall visibility.
7. Leverage Image Titles and Captions
Image titles and captions can provide additional context, enhancing both user engagement and SEO. While not as critical as alt text, titles can offer search engines more information about the image’s purpose. Captions, often seen directly below images, are one of the first places users look when scanning a page.
Captions should be descriptive and relevant, helping users better understand the image and its connection to the content. When used effectively, they can keep users engaged longer, which contributes to better SEO performance.
8. Use Image Structured Data

Example of image structure data from Google Search Central.
Structured data, such as Schema.org markup, helps search engines understand images more effectively, providing additional details about the image. This can be particularly useful for images of products or recipes, where details like price or cooking time can be included in the markup.
By adding structured data to your images, you increase the likelihood that they’ll appear in rich snippets or Google Image search results, providing a competitive edge in search rankings.
9. Create and Submit Image Sitemaps
Image sitemaps are a helpful tool in ensuring that search engines can discover and index all images on your website. Submitting an image sitemap to Google provides search engines with a map of where your images are located, improving the chances of those images appearing in image searches.
Ensure images are able to be opened in a new tab on their own – this enables search engines to crawl and index images, allowing them to be displayed in image search results. If an image doesn’t have its own URL, it won’t be able to be included in an image sitemap or in search results.
Tools like Google Search Console and Screaming Frog can help you generate these sitemaps quickly. Including alt text and metadata within your sitemap further enhances image SEO.
10. Mobile Image Optimization
Using responsive images ensures that different image sizes load depending on the user’s screen size, improving performance.
Implementing the srcset attribute allows browsers to choose the best version of an image for each device, making your site faster on mobile devices.
Additionally, compressing and resizing images specifically for mobile helps reduce load times and ensures a smooth browsing experience on smaller screens.
Reach Out to Simple Search for Expert SEO Image Optimization
Image optimization is an essential aspect of SEO, contributing to better page speed, user experience, and search rankings. By following these steps, you can enhance your website’s performance and improve its visibility in search results.
Regularly auditing your images and applying these best practices ensures your content remains optimized for both users and search engines, helping you stay competitive in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Simple Search Marketing’s SEO experts regularly audit images to improve image SEO and save time while improving organic performance. See how we can help you.

